Aceraceae/Sapindaceae – Maple Family
In 2024, this Florida Maple measured 52 feet tall and 35 inches in diameter. Based on USDA Forest Service models, it will absorb approximately 576 lbs. of carbon over the next 20 years. Put simply, this tree alone will offset up to 2,331 car miles worth of carbon dioxide.
See all species on the Campus Tree Tour.
Introduction
The Florida maple, also known as the southern sugar maple, is found in the forest sub canopy and along sidewalks in city parks of the Southeastern United States. Compared to its northern counterparts, the Florida maple is not used to produce maple syrup. During the summer the foliage is bright green, and in the fall, the leaves display red, orange, and yellow hues.
Physical Description
Life expectancy: Up to 130 years
Height: 50-60 feet
Crown: Can spread from 25-40 feet
Diameter: Up to 35 inches
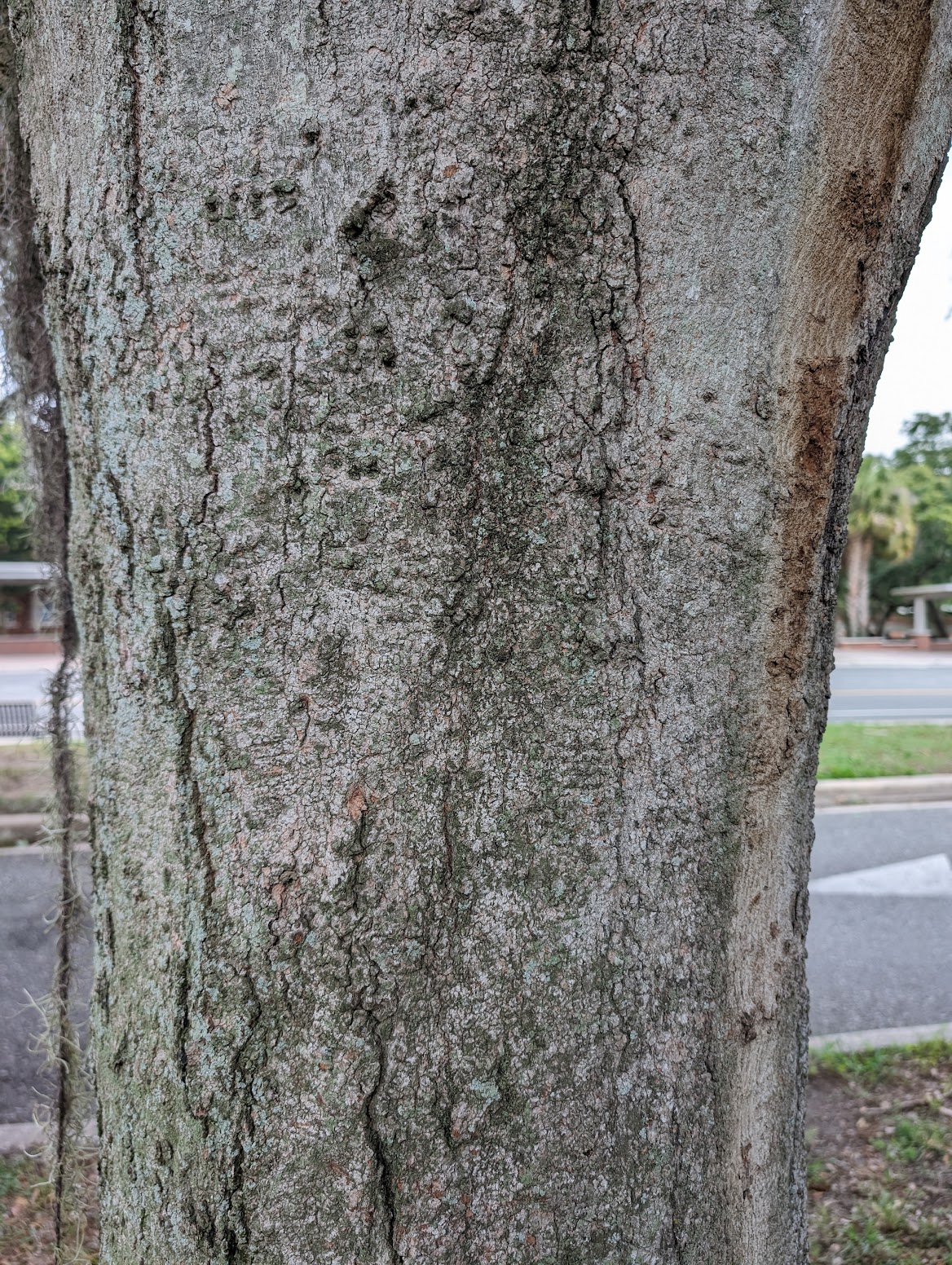
Bark: Tan, thin bark with shallow fissures, becomes blockier as it matures.
Leaves: Deciduous, simple, and oppositely arranged upon the twig. The green leaves have pale white undersides, and they are star-shaped from lobing. The edges, or margins, between the lobes are smooth and entire.
Flowers: Yellow-green flowers that form clusters on the ends of branches in early spring.
Fruits: Green to reddish-brown paired samaras that grow up to 1 ½ inches upon reaching maturity in mid-summer.
Key Identification Characteristics: Opposite leaf arrangement, star-shaped leaves with entire margins and pale undersides, thin bark.
Past and Present Uses
The Florida maple is not managed as a commercial timber species, nor is it used for sugar production. However, it may be used in niche markets with associated commercial species for pulpwood, furniture, and cabinetry. Most commonly, the tree’s ability to tolerate various soil types and its strong, wind-resistant limbs make it an ideal shade or street tree in urban landscaping. Since its roots grow near the surface, it is recommended that the Florida maple is not planted in an area that needs intensive mowing to avoid damage.
Ecological Importance
Origin: Native to the United States
Native Range: Found from southeastern Virginia through the Carolinas to northern Florida; west to Texas and Oklahoma.
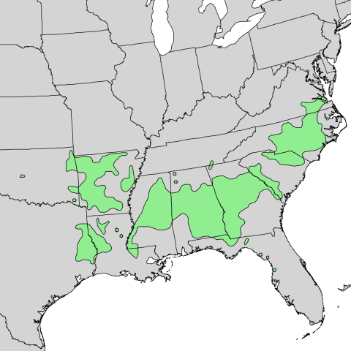
Figure 1. Native range of Florida Maple. Photo credit: U.S. Geological Survey
Florida maples are found growing in mesic hardwood hammocks and sloped forests, preferring well drained and calcium rich soils. It is a major component of the understory and will not dominate the canopy since it is shade tolerant. It is found in drier sights compared to its relative, red maple, which is found in areas closer to water. Within the hammock, the Florida maple is commonly associated with sweetgum, water oak, southern red oak, ash, loblolly pine, and cabbage palm.
Florida maple flowers bloom in early spring, serving as a source of nectar for bees and other pollinators. The seeds from the samaras offer a food source for birds, squirrels, and deer while its trunk and canopy can be used as a comfortable habitat for small animals.
More Information
https://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/publication/ST007
References
Acer floridanum (Florida Maple). Gardenia. (n.d.). https://www.gardenia.net/plant/acer-floridanum
Cook, W. (2015). Southern sugar maple (Acer floridanum). Carolina Nature. https://www.carolinanature.com/trees/acfl.html
Gilman, E. F., Watson, D. G., Klein, R. W., Koeser, A. K., Hilbert, D. R., & McLean, D. C. (2019). ENH166/ST007: Acer Floridanum: Florida maple. Ask IFAS - Powered by EDIS. https://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/publication/ST007
i-Tree. (2006). Tree tools - calculate the benefits of trees!. i-Tree. https://www.itreetools.org/
Jones, E. R. (n.d.). Florida maple. Acer barbatum Michx. https://www.srs.fs.usda.gov/pubs/misc/ag_654/volume_2/acer/barbatum.htm
NC State Extension. (n.d.). Acer saccharum subsp. floridanum. North Carolina Extension Gardener Plant Toolbox. https://plants.ces.ncsu.edu/plants/acer-saccharum-subsp-floridanum/



